Diagram of the male sex cells sperm Royalty Free Vector
How is the body of a sperm suited for fertilization of an egg? Socratic
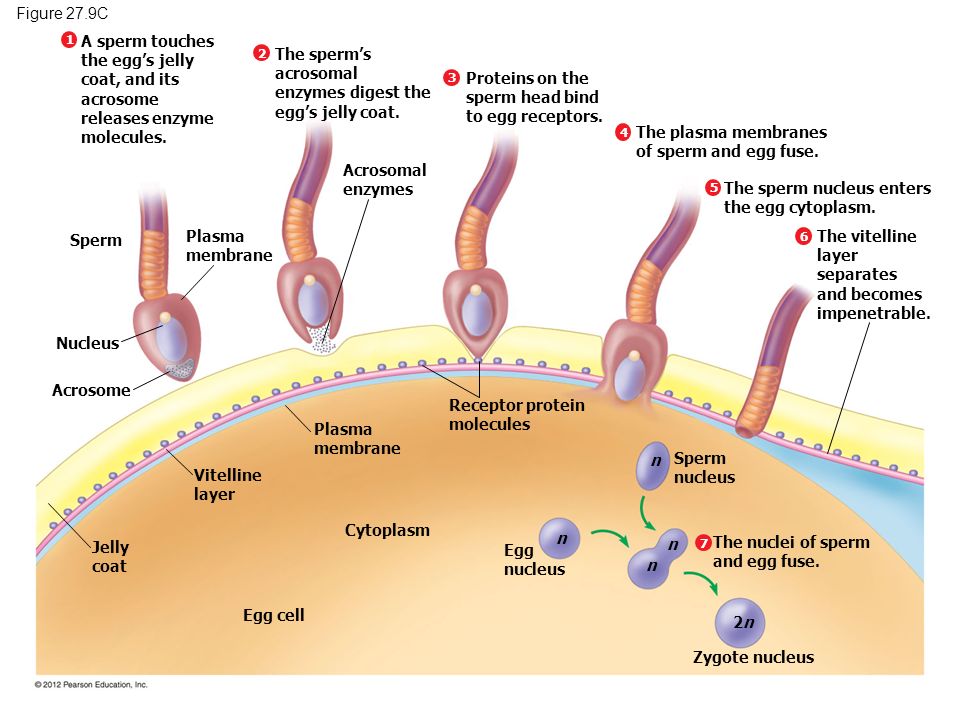
A sperm cell attempting to penetrate an egg (ovum) to fertilize it. The head of the sperm varies in shape for each animal species. In humans it is flattened and almond-shaped, four to five micrometres long and two to three micrometres wide (there are about 25,000 micrometres in an inch).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/azoospermia-overview-4178823-5c5db5ffc9e77c00010a486a.png)
What Your Semen Says About Your Health
The following is an overview of the male reproductive anatomy: Scrotum. The bag of skin that holds and helps to protect the testicles. The testicles make sperm and, to do this, the temperature of the testicles needs to be cooler than the inside of the body. This is why the scrotum is located outside of the body. Click image to enlarge.
Signaling mechanisms in mammalian sperm motility†
In most species, there are just two types of gamete, and they are radically different. The egg is among the largest cells in an organism, while the sperm (spermatozoon, plural spermatozoa) is often the smallest. The egg and the sperm are optimized in opposite ways for the propagation of the genes they carry. The egg is nonmotile and aids the survival of the maternal genes by providing large.

Fertilization Sperm Cell Of The Egg Stock Vector Art & More Images of Acrosome
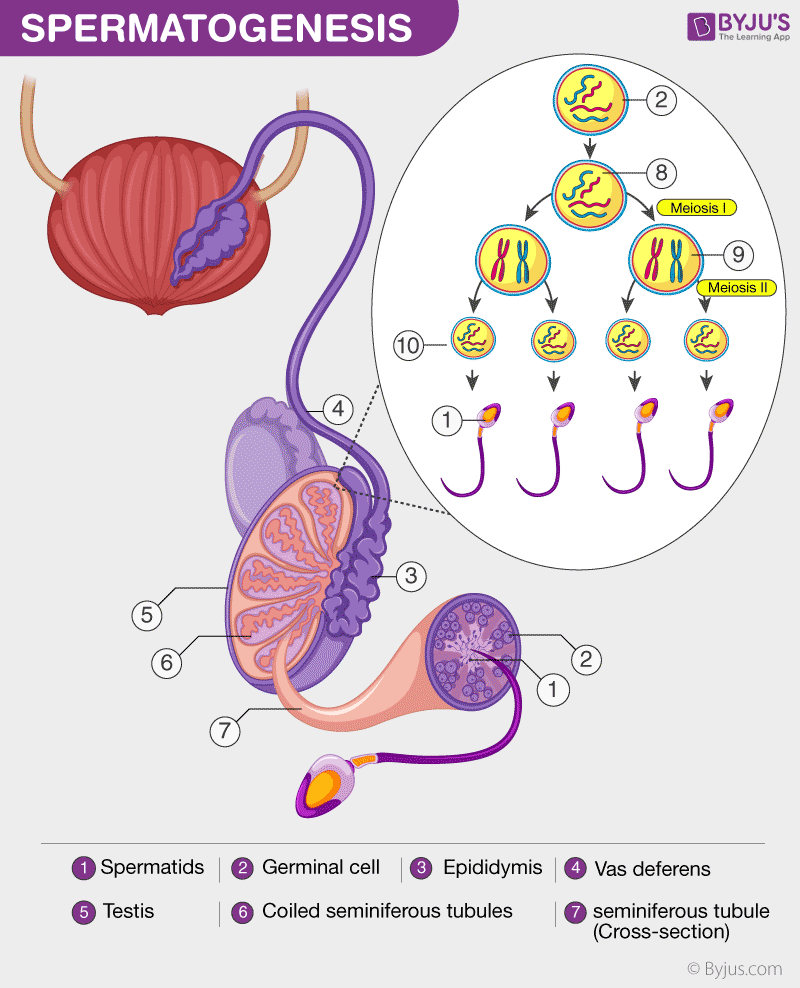
Sperm is the male reproductive cell or gamete. The term "gamete" implies that the cell is half of a whole. When a sperm combines with a female gamete, or egg, it results in a human embryo.
Spermatogenesis The Purpose and Process of Spermatogenesis
Diagram of a human sperm cell Sperm ( pl.: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one).
Labeled Sperm Cell Illustrations, RoyaltyFree Vector Graphics & Clip Art iStock
AboutTranscript. This video explores the journey of sperm from the male reproductive system to the female reproductive system. It details the two-step process of erection and ejaculation, explaining the role of the brain and blood vessels in achieving an erection. The video also delves into the anatomy of the penis and the process of ejaculation.

The Long, Winding Tale of Sperm Science Science Smithsonian
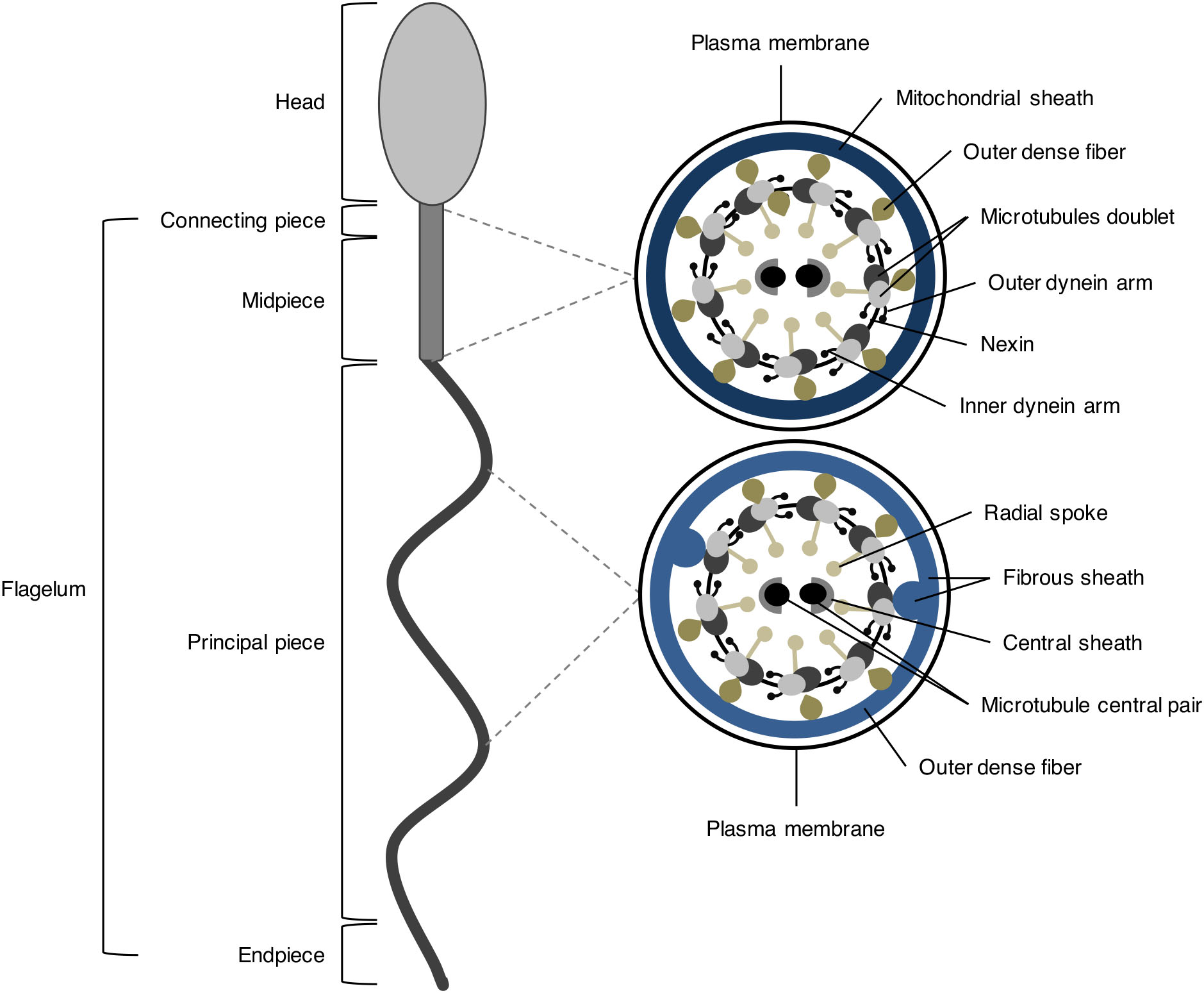
Human sperm is a microscopic structure whose shape is like a tadpole. It has flagella which make it motile. Its diameter is 2 - 5 μ m, and its length is 60 μ m. It is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It has no nutritional material. It lacks most cell organelles like ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, etc.
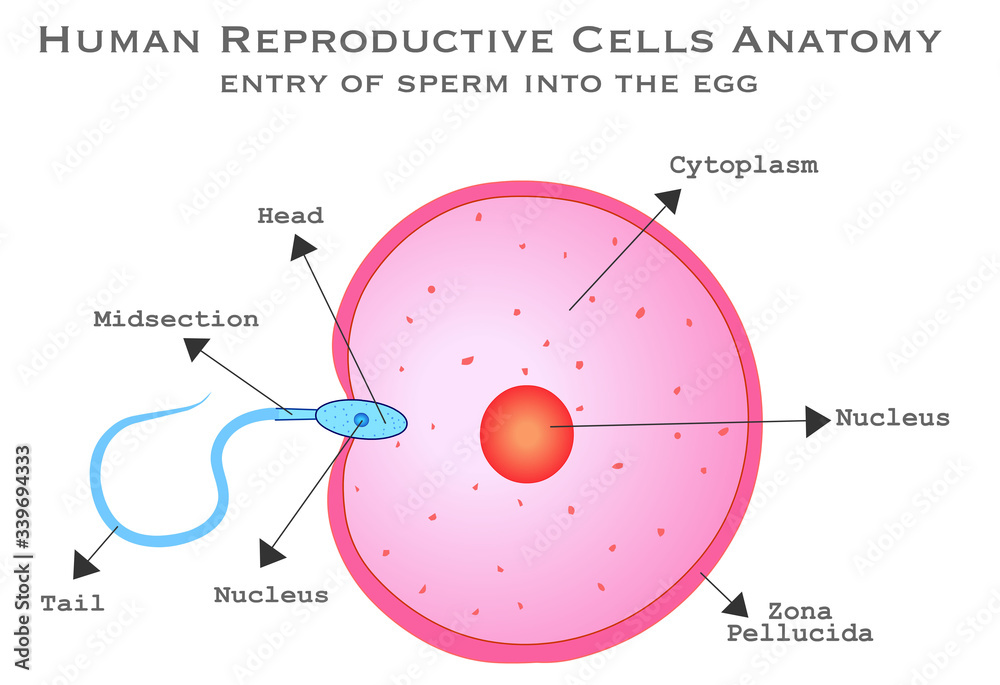
Human male female reproductive cells diagram. Fertilizer. Sperm cell entry into the ovum cell
H = diagram of the sperm flagellum showing the orientation of the sections shown in F and G; the location of the linear arrangement of CatSper is shown in red: the domains run along each side of the longitudinal columns of the sperm flagellum, ODF outer dense fibre All images are reproduced from Chung et al. with permission.
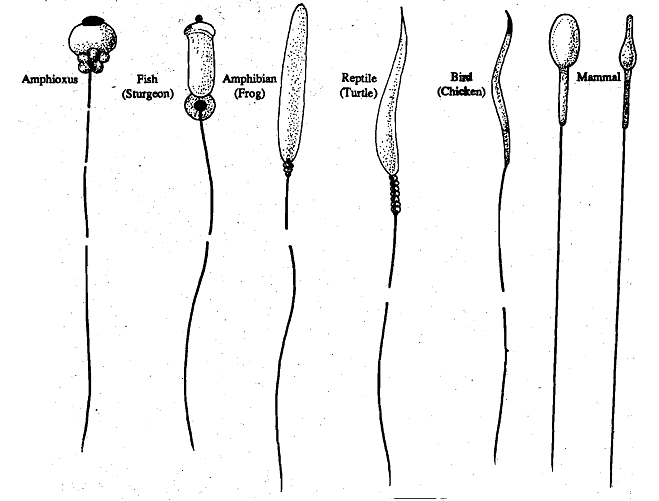
Structure of the sperm, Structure of the Sperm The spermatozoa in different animal, Biology
Sperm cells are gametes (sex cells) that are produced in the testicular organ (gonad) of male human beings and animals. Like the female gamete (oocyte), sperm cells carry a total of 23 chromosomes that are a result of a process known as meiosis. In both animals and human beings, among many other organisms, these cells are involved in the sexual.

The Male and Female Reproductive Systems Berne and Levy Physiology, 6th ed
Human Sperm: Detailed and labeled diagram of a human spermatozoa. Fertility Factors. Sperm quantity and quality are the main parameters in semen quality, a measure of the ability of semen to accomplish fertilization. The genetic quality of sperm, as well as its volume and motility, all typically decrease with age..

Draw the diagram of human sperm and label its parts. Write a few lines about it.
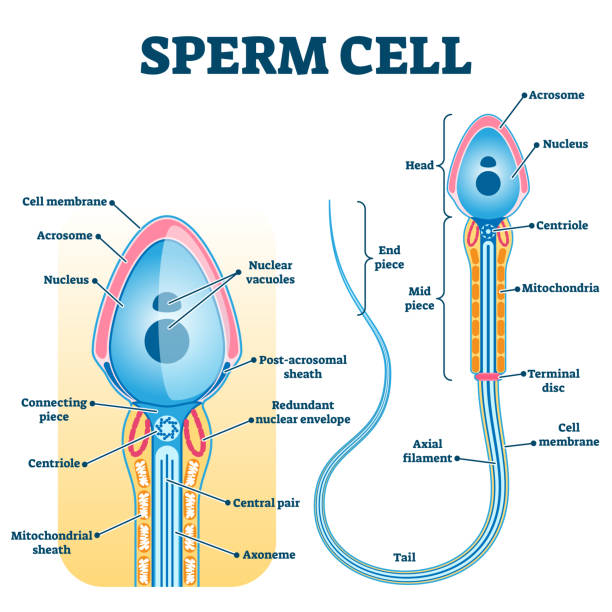
Short answer annotated diagram of sperm cell: A sperm cell has three parts - the head, midpiece, and tail. The head contains the genetic information, while the midpiece produces energy for movement and the tail propels it forward. The acrosome at the tip of the head contains enzymes that help penetrate an egg during fertilization. […]

Fertilization Egg Activation, Sperm Fusion, Zygote Britannica
Figure 22.3. 2: Male Reproductive System The structures of the male reproductive system include the testes, the epididymis, the penis, and the ducts and glands that produce and carry semen. Sperm exit the scrotum through the ductus deferens, which is bundled in the spermatic cord. The seminal vesicles and prostate gland add fluids to the sperm.
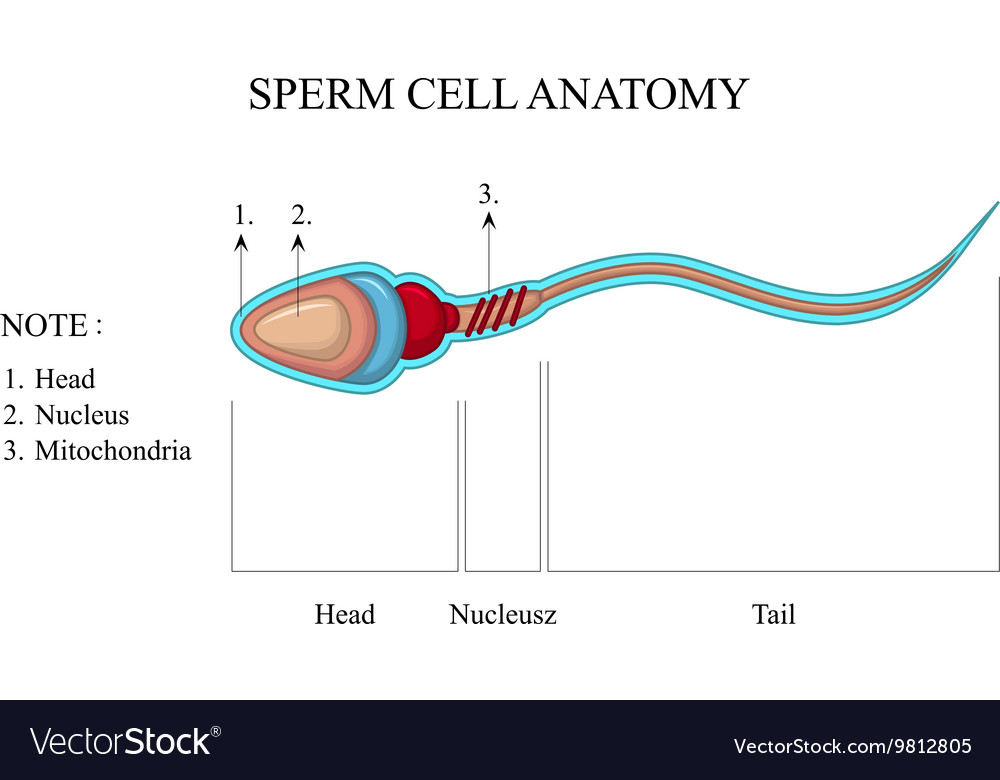
Human sperm cell anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image
A spermatozoon, in plural spermatozoa, or sperm cell is the male reproductive cell that is produced in the man´s testicles in a process called spermatogenesis. The sperm cell´s function is to enable sexual reproduction through its union with the female egg during fertilization.
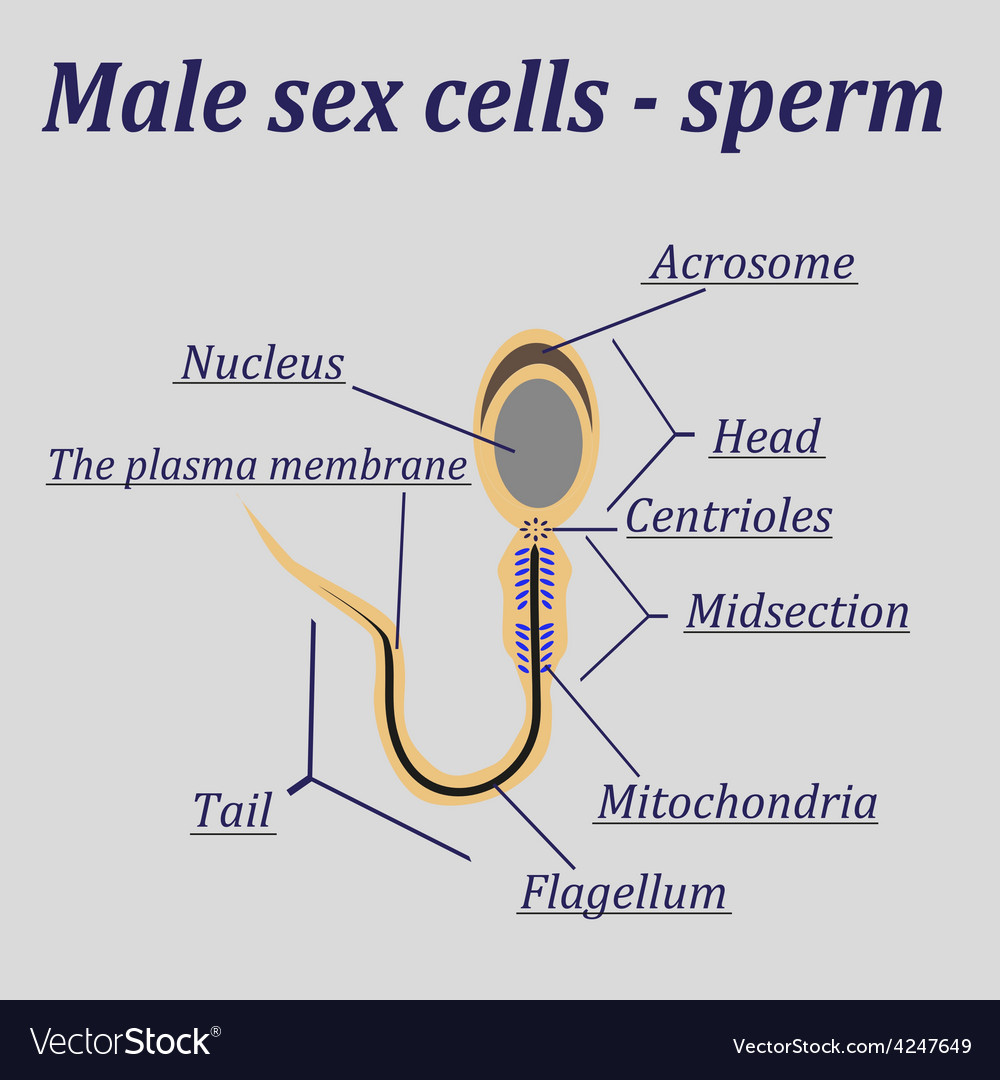
Diagram of the male sex cells sperm Royalty Free Vector
A mature sperm cell has several structures that help it reach and penetrate an egg. These are labeled in the drawing of a sperm shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). The head is the part of the sperm that contains the nucleus — and not much else. The nucleus, in turn, contains tightly coiled DNA that is the male parent's contribution to the.

sperm cell Diagram Quizlet
This labelled diagram shows the structure of a sperm cell in detail, which has the following parts: Head With its spheric shape, it consists of a large nucleus, which at the same time contains an acrosome. The nucleus contains the genetic information and 23 chromosomes.
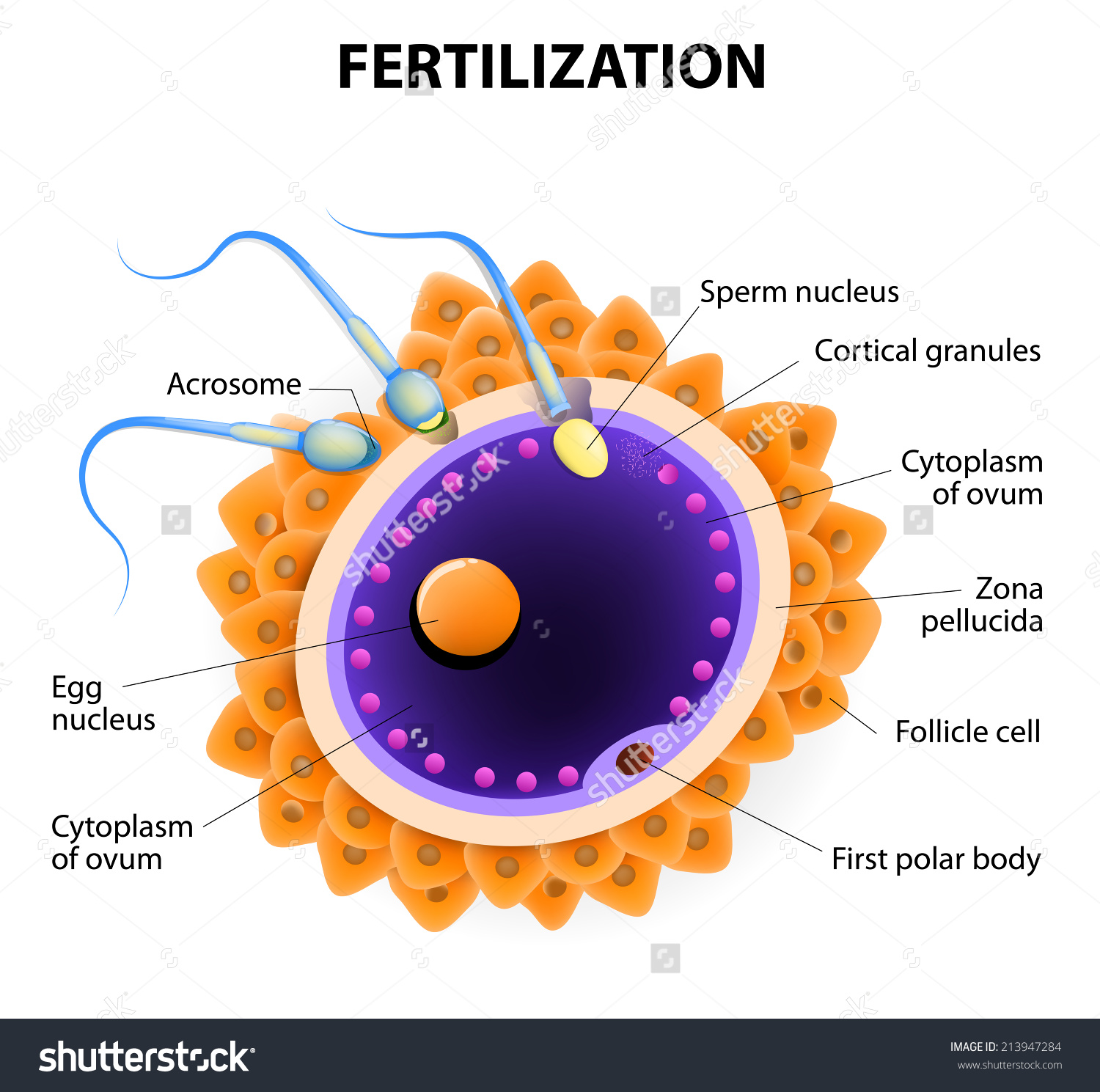
What is the process of sperm and egg combining called? Socratic
The sperm cell diagram below shows multiflagellate fern cells. Sperm cells from the fern plant. Most motile spermatozoa have flagella to help them swim through fluids - the seminal fluid produced by males and the mucus membranes of the female reproductive tract. Flagellum movement requires a consistent energy source.